The shoulder is a particularly complex joint in its anatomy and function, with an infinite number of possible pathologies and combinations, but there are a series of problems that are repeated with special frequency,” Gonzalo Samitier, orthopedic surgeon, head of the Member Unit explains to CuídatePlus Superior of the General Hospital of Villalba (Madrid) and expert in shoulder, knee and arthroscopy surgery.

Most frequent causes of shoulder pain
The repetitive movements and lack of ergonomics are two of the causes that can provoke pain in the shoulder, both at work level, as domestic or sports. Also, direct trauma to the joint itself may be another of the most relevant causes, according to Milagros Casado and Sandra Iturralde, director and physiotherapist responsible, respectively, of the Rehabilitation Service of the University of Navarra Clinic (CUN) at its headquarters in Pamplona.
Samitier states that if we except for fractures and dislocations secondary to trauma and focus on shoulder pain with no history of stroke or obvious effort, the most common problems are:
• In the youngest, below 30-40 years, especially the most sportsmen, the most common are the problems of the glenoid labrum. Pain is more limiting with intense physical activity or repetitive movements. Injury to the labrum in the upper region is called ‘SLAP injury’ and is especially common because the long portion of the biceps tendon is inserted right there. Sometimes these patients have a history of shoulder instability, that is, the shoulder “comes out” of their place (partially or totally) and they end up further injuring the labrum and the ligaments that hold this joint in place.
• Above 50 to 75 years, the most common is rotator cuff pathology, which causes damage to the lateral aspect of the shoulder when it is damaged and very often night pain. Tendons may simply be inflamed ( tendinitis), present calcifications (calcifying tendinitis), or reach the rupture that may be partial or complete.
When there is a complete rupture of one or more tendons and when conservative treatment (through rehabilitation, anti-inflammatories, and corticosteroid infiltrations) is not effective for months, with the person still very limited and in pain, arthroscopic surgery is often the best option. by a shoulder specialist, who will be able to offer us the best results based on our injury. The long biceps tendon is also frequently damaged in these patients, but it can be treated at the same time as the other tendons during the intervention.
• Above 75 years of age what we usually find in the consultation are patients with osteoarthritis. Primary, for no apparent reason other than the passing of the years, or secondary to the long-term rupture of the mentioned tendons. If the patient is very limited, and conservative treatments are not effective, the shoulder prosthesis offers excellent results and a marked improvement in the quality of life.
Sports and postural habits
The head of the Superior Member Unit of the General Hospital of Villalba then talks about how sport and postural habits influence shoulder injuries.
1. Sport and intense physical work, where the shoulder joint predominantly intervenes, can clearly trigger problems in the medium-long term. In youth, launch, contact or wrestling sports often cause problems with the labrum or inflammation and wear of the rotator cuff, which requires an intervention to repair these structures if you want to continue practicing the sport at a high intensity level. .
However, the same injury in the patient who is not very active or who decides to decrease the intensity and frequency of their physical or sports activity, is usually well tolerated and requires nothing more than rehabilitative treatment and observation over time.
It is different when there is a complete rupture of one or more tendons of the rotator cuff. In these cases, the younger the patient, especially below 55-60 years, the higher the recommendation for restorative surgery because over time the injury becomes larger and the prognosis of the surgery, which is usually very favorable initially, worsens if the injury is treated too late.
2. Postural habits they do not really cause injuries to the shoulder, what does happen is that an already damaged shoulder when we lean on it or subject it to certain positions, the pain intensifies. This is very characteristic of people with rotator cuff problems; night pain prevents them from resting and is very frustrating due to the inability to get adequate rest.
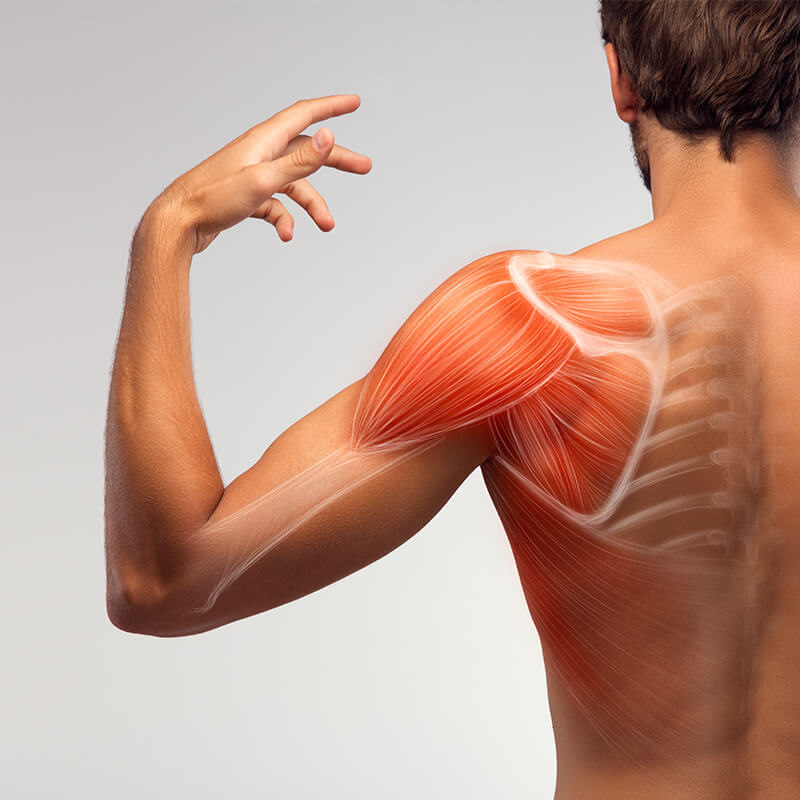
Also, those professionals who make repetitive efforts, always in the same position, raising the arms or leaning them forward, can eventually damage the shoulder tendons by always overloading the same structures and because there is the friction of the tendons against the acromion -a bone area of the scapula that forms the roof of the joint and is easily palpable in the upper part of the shoulder.
For Casado and Iturralde, both circumstances can cause shoulder injuries. “The practice of sports that involve greater explosiveness and speed of movements, such as throwing, tennis, paddle tennis, basketball, handball, if they are not accompanied by good postural habits or a good throwing technique, can lead to injuries on a said joint”.
What to do when shoulder pain appears?
The first thing, says Samitier, is to differentiate if it was an acute injury triggered by an effort or fall or if it is an injury that has appeared progressively.
In the most disabling traumatic injuries, at least one x-ray must be performed and a nuclear magnetic resonance is usually advisable or, failing that, an ultrasound to rule out bone fractures, dislocations, tendon, ligament or labrum injuries, among others. .
If the pain has come on progressively, but is not very limiting, simply slowing down nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and gentle mobility and strength exercises may suffice. Rehabilitation and/or physical therapy is of great help in these patients and recommended exercises should be maintained for three to six months, before considering that conservative treatment is not working.
The infiltrations can be very effective in the mildest cases of inflammation of the tendons but are not so when there is a complete tear of a tendon or labrum, in which case the final solution is surgery.
In any case, it concludes the traumatologist at the General Hospital of Villalba, it must be borne in mind again that the causes of shoulder pain are many and that some of them are not easy to identify. “So we just accept diagnoses and treatment recommendations by a shoulder specialist who also has studied our case, made a detailed physical examination and access to imaging tests our shoulder.”
The CUN experts reinforce this recommendation, noting that the patient “should be evaluated by a specialist doctor to have a good diagnosis of said pathology.”
What if that pain remains?
“If the shoulder pain remains and if it is disabling despite rest, anti-inflammatory drugs, infiltrations and/or a period of rehabilitation and physiotherapy of at least three months, then we speak of a failure of conservative treatment. It is then time to consult a shoulder specialist, following an individualized approach for each injury and patient. In expert hands, it can be said that today there is a solution for the vast majority of shoulder problems, “says Samitier.
“In addition to being assessed by a doctor or specialist professional, excessive activity on the joint should be avoided, as much as possible, whether it be in the workplace, sports, or related causes. It would also be advisable to adopt good habits advised by a qualified professional ”, indicate Casado and Iturralde.
The importance of rest and how it should be
“Shoulder rest is advisable after an effort or trauma that has caused pain and inflammation, but often it should not be an absolute rest because it leads to stiffness and muscle atrophy that will later cost a lot to overcome,” he says. Samitier.
In most cases, this specialist explains, it is about making an active rest in which gentle mobility exercises of the elbow, pendulum movements, lifting of the arm with help, and, in the end, exercises of strengthening. Such exercises to enhance the shoulder and scapula muscles – whether with rubber bands, pulleys, or in the pool – and to have the shoulders in a correct back position, are highly recommended in almost any problem of this joint.

Steps of treatment
Samitier insists that the main thing is a good diagnosis , “without it we run the risk of under- or over-treatment of the injury. The first measure to alleviate shoulder pain is usually rest , and secondly , oral pain relievers and anti-inflammatories and rehabilitation associated with physical therapy techniques.
If none of this is effective, the last step before intervention would be joint infiltration, which consists of one or more injections, usually corticosteroid plus local anesthetic, in the injured and painful area. Although this is not always recommended, especially if we are going to end up in surgery as well ”.
Regarding rehabilitation, the CUN recalls that “there are many techniques applied to relieve pain, in addition to rest and the most convenient advice regarding the activity that the patient performs. It is also important to coordinate jointly with the rehabilitating doctor, who, in addition to diagnosing the patient’s pathology, can prescribe a pharmacological treatment to optimize his analgesia ”.
 The Care Up
The Care Up




